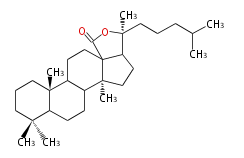Category:TP3
(→Design of Tri-terpene ID numbers ID番号の設計) |
m (→Biosynthesis) |
||
| Line 50: | Line 50: | ||
==Biosynthesis== | ==Biosynthesis== | ||
{{Twocolumn| | {{Twocolumn| | ||
| − | The starting point is | + | The starting point is squalene, which is formed by joining two FPPs tail-to-tail. |
| − | This molecule undergoes cyclization | + | In bacteria, squalene is cyclized via the 17α-deoxydammarenyl cation to hopene and other triterpenes. |
| + | In eukaryotes, 2,3-oxidosqualene is cyclized via the protosteryl cation to lanosterol or cycloartenol by a series of 1,2-hydride and methyl shifts (Wagner-Meerwein shifts). | ||
| + | Plant triterpenes arise from the dammarenyl cation. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | This molecule undergoes cyclization to form either the protosterol cation (through chair-boat cyclization) or the dammarenyl cation (through chair-chair cyclization). | ||
| + | From the protosterol cation, lanosterol or cycloartenol occurs. | ||
| + | From the 17β-dammarenyl cation, dammarane and other plant triterpenoids occur. From the 17α-damarenyl cation, hopanoids occur. | ||
; animals, fungi, and yeast | ; animals, fungi, and yeast | ||
: 2,3-oxidosqualene → lanosterol | : 2,3-oxidosqualene → lanosterol | ||
| Line 59: | Line 66: | ||
: 2,3-oxidosqualene → hopene | : 2,3-oxidosqualene → hopene | ||
| | | | ||
| − | + | 始まりとなる物質はスクアレンで、二分子のファルネシル二リン酸が末尾どうしで結合して作られます。 | |
| − | + | ||
| + | バクテリアが合成するホパノイドはスクアレンがそのまま環化して生じ、 | ||
| + | |||
| + | 2,3-オキシドスクアレンが環化する際に、ABC環が椅子-舟-5員環となる構造がまず生じ、椅子型C環へ拡張された後に5員型D環が生じたものがプロトステロールカチオン (椅子-舟-椅子-5員環) です。 | ||
| + | このカチオンからメチル基の転位反応を経て (Wagner-Meerweinシフト)、ラノステロールおよびシクロアルテノール (ともに椅子-椅子-椅子-5員環) が生じます。 | ||
| + | ダンマラン型の骨格は、2,3-オキシドスクアレンが環化する際に、椅子-椅子-椅子-5員環の構造がそのまま生じます。 | ||
| + | ホパノイドは複雑で2回の環拡張をおこないます。 | ||
| + | |||
| + | 骨格転位反応 (Wagner-Meerwein shift) を起こし、種ごとに異なる前駆体を形成します。 | ||
; 動物、カビ、酵母 | ; 動物、カビ、酵母 | ||
: 2,3-オキシドスクアレン → ラノステロール | : 2,3-オキシドスクアレン → ラノステロール | ||
| Line 68: | Line 83: | ||
: 2,3-オキシドスクアレン → ホペン | : 2,3-オキシドスクアレン → ホペン | ||
}} | }} | ||
| + | ====Cyclization==== | ||
| + | <center> | ||
| + | {|style="text-align:center" | ||
| + | | squalene | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | 2,3-oxidosqualene | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [[Image:squalene.png]] | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | [[Image:2,3-oxidosqualene.png]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [[Image:Arrow35d.png]] | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| style="text-align:center" | ||
| + | | [[Image:cycloartenol.png]]<br/>cycloartenol<br/><small>(chair-boat + ring expansion)</small> | ||
| + | | rowspan="3" | | ||
| + | <math>\longleftarrow</math><br/>PLANTS<br/> | ||
| + | <br/>PLANTS<br/><math>\longleftarrow</math> | ||
| + | | rowspan="3" | [[Image:2,3-oxidosqualene.png]]<br/>2,3-oxidosqualene | ||
| + | | rowspan="3" | | ||
| + | <math>\longrightarrow</math><br/>ANIMALS, FUNGI<br/> | ||
| + | <br/>BACTERIA<br/><math>\longrightarrow</math> | ||
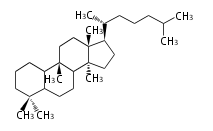
| + | | [[Image:lanosterol.png]]<br/>lanosterol | ||
| + | |- | ||
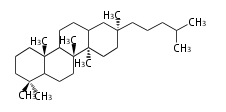
| + | | [[Image:dammarane.png]]<br/>dammarane<br/><small>(chair-chair + ring expansion)</small> | ||
| + | | [[Image:hopene.png]]<br/>hopene | ||
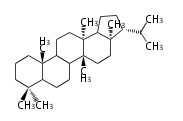
| + | |} | ||
<ref>Ohyama K, Suzuki M, Kikuchi J, Saito K, Muranaka T “Dual biosynthetic pathways to phytosterol via cycloartenol and lanosterol in Arabidopsis” Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(3):725-730, 2009</ref> | <ref>Ohyama K, Suzuki M, Kikuchi J, Saito K, Muranaka T “Dual biosynthetic pathways to phytosterol via cycloartenol and lanosterol in Arabidopsis” Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(3):725-730, 2009</ref> | ||
Revision as of 14:44, 5 August 2010
Contents |
Triterpene (C30) Classes
Ring configuration
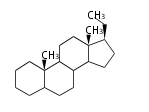
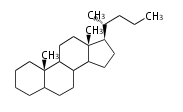
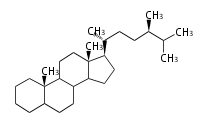
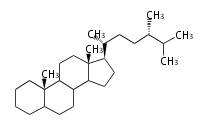
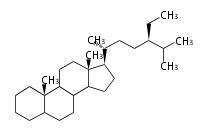
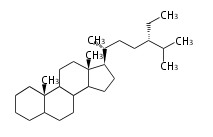
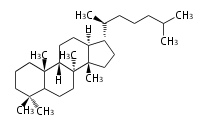
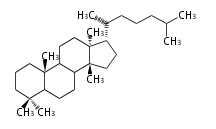
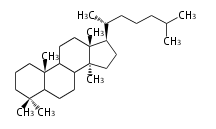
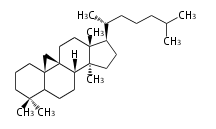
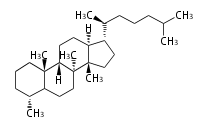
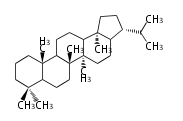
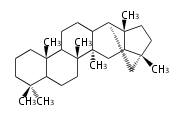
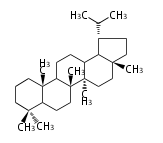
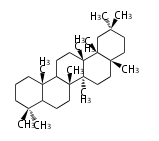
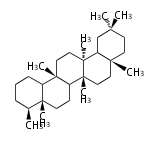
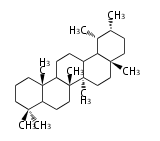
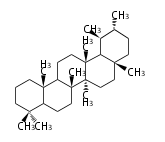
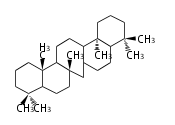
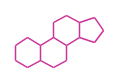
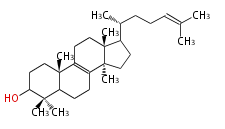
The basic structure is 4 carbon rings, cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene, gonane, or sterane. The rings B/C are always trans in all natural steroids. If the rings C/D are trans, it is called gonane. If its stereochemistry is unspecified, it is called sterane. Most steroids take gonane form, but in cardenolides and bufanolides, the rings C/D are cis.
 |
|
| Cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene | Gonane |
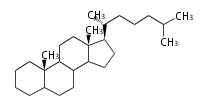
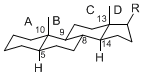
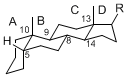
The majority of steroids have methyl groups sticking out from the bridgehead positions C-10 and C-13. When these methyl groups (or hydrogens) stand above the plane, they are called β-configuration. Those below the plane are called α-configuration. If the configuration at any site is unknown, it is indicated as ξ (Greek Xi). By default, hydrogen atoms or substituents at the positions C-8, 9, 10, 13, and 14 are assumed to be 8β, 9α, 10β, 13β, and 14α configurations. C-5 is a special position, because there are as many 5α steroids as 5β are.
 |
 |
|
| cholestane backbone | 5α-configuration | 5β-configuration |
Biosynthesis
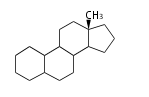
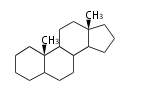
The starting point is squalene, which is formed by joining two FPPs tail-to-tail. In bacteria, squalene is cyclized via the 17α-deoxydammarenyl cation to hopene and other triterpenes. In eukaryotes, 2,3-oxidosqualene is cyclized via the protosteryl cation to lanosterol or cycloartenol by a series of 1,2-hydride and methyl shifts (Wagner-Meerwein shifts). Plant triterpenes arise from the dammarenyl cation. This molecule undergoes cyclization to form either the protosterol cation (through chair-boat cyclization) or the dammarenyl cation (through chair-chair cyclization). From the protosterol cation, lanosterol or cycloartenol occurs. From the 17β-dammarenyl cation, dammarane and other plant triterpenoids occur. From the 17α-damarenyl cation, hopanoids occur.
- animals, fungi, and yeast
- 2,3-oxidosqualene → lanosterol
- plants (including algae)
- 2,3-oxidosqualene → cycloartenol, dammarane
- bacteria
- 2,3-oxidosqualene → hopene
Cyclization
| squalene | 2,3-oxidosqualene | |
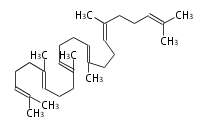
|
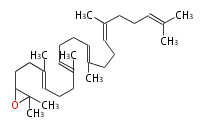
| |
| File:Arrow35d.png | ||
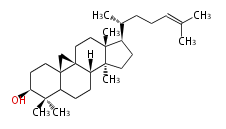 cycloartenol (chair-boat + ring expansion) |
|
 2,3-oxidosqualene |
|
 lanosterol |
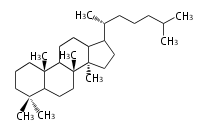 dammarane (chair-chair + ring expansion) |
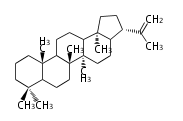 hopene |
Design of Tri-terpene ID numbers ID番号の設計
<center> 12-DIGIT
| T | P | 3 | x | y | y | r | h | g | n | c | c |
- x ... species information
| Symbol at x | Kingdom | Phyla | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | Animalia | Arthropoda (Insects, crabs) | ecdysteroids |
| V | Chordate (Vertebrates) | sex steroids, corticosteroids, anabolic steroids | |
| O | Others | marine steroids | |
| P | Plantae | Phytosterols | lanosterols, cholesterols, brassinolides |
| S | Saponins | saponins | |
| F | Fungi | ergosterols | ergosterols |
| B | Bacteria | bacterial sterols | hopanoids |
- y ... backbone structure (母核構造)
- r ... number of major rings (環構造数)
Click above categories to see details.
- h ... hydroxylation pattern (水酸基数)
Click above categories to see details.
- g ... glycosylation pattern(糖修飾パターン)
Click above categories to see details.
- n ... number of sugars (修飾糖数)
Click above categories to see details.
- c ... serial number (通し番号)
Cite error:
<ref> tags exist, but no <references/> tag was found
This category currently contains no pages or media.