Category:TP3
m (→Biosynthesis) |
m (→Biosynthesis) |
||
| Line 77: | Line 77: | ||
| lupeol [[Image:Arrow00dr35.png]] synthase | | lupeol [[Image:Arrow00dr35.png]] synthase | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 17β-protosteryl cation<ref>The rings of protosteryl cation are chair-boat-chair configuration. The C-17 chain is β-configuration, not α.<br/> | + | | 17β-protosteryl cation <small>(C-B-C)</small><ref>The rings of protosteryl cation are chair-boat-chair configuration. The C-17 chain is β-configuration, not α.<br/> |
''Ref.'' Corey EJ, Virgil SC (1991) An experimental demonstration of the stereochemistry of enzymic cyclization of 2,3-oxidosqualene to the protosterol system, forerunner of lanosterol and cholesterol. [http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/ja00010a073 ''J Am Chem Soc'' 113:4025-6]</ref> | ''Ref.'' Corey EJ, Virgil SC (1991) An experimental demonstration of the stereochemistry of enzymic cyclization of 2,3-oxidosqualene to the protosterol system, forerunner of lanosterol and cholesterol. [http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/ja00010a073 ''J Am Chem Soc'' 113:4025-6]</ref> | ||
<br/>[[Image:Protosteryl cation.png]] | <br/>[[Image:Protosteryl cation.png]] | ||
|rowspan="2"| D-ring<br/>expansion<br/>[[Image:Arrow00r35.png]]<br/>+ E-ring<br/>cyclization<br/>(from 18α/17β) | |rowspan="2"| D-ring<br/>expansion<br/>[[Image:Arrow00r35.png]]<br/>+ E-ring<br/>cyclization<br/>(from 18α/17β) | ||
| − | |rowspan="2"| hancolupyl | + | |rowspan="2"| hancolupyl cat. <small>(C-B-C-C)</small><br/>[[Image:Hancolupyl cation.png|150px]]<br/>arborinyl cation <small>(C-B-C-C)</small><br/>[[Image:Arborinyl cation.png|150px]] |
| | | | ||
| − | | 17β-dammarenyl cation<ref>The rings of dammarenyl cation are all-chair configuration. The C-17 chain is β-configuration.<br/> | + | | 17β-dammarenyl cation <small>(C-C-C)</small><ref>The rings of dammarenyl cation are all-chair configuration. The C-17 chain is β-configuration.<br/> |
''Ref.'' Xiong Q, Rocco F, Wilson WK, Xu R, Ceruti M, Matsuda SPT (2005) Structure and reactivity of the dammarenyl cation: configuration transmission in triterpene synthesis. ''J Org. Chem. 70:5362-75</ref> | ''Ref.'' Xiong Q, Rocco F, Wilson WK, Xu R, Ceruti M, Matsuda SPT (2005) Structure and reactivity of the dammarenyl cation: configuration transmission in triterpene synthesis. ''J Org. Chem. 70:5362-75</ref> | ||
<br/>[[Image:Dammarenyl cation.png]] | <br/>[[Image:Dammarenyl cation.png]] | ||
| D-ring<br/>[[Image:Arrow00r35.png]]<br/>expansion | | D-ring<br/>[[Image:Arrow00r35.png]]<br/>expansion | ||
| − | | baccarenyl cation<br/>[[Image:Baccarenyl cation.png]] | + | | baccarenyl cation <small>(C-C-C-C)</small><br/>[[Image:Baccarenyl cation.png]] |
|- | |- | ||
|align="center"| | |align="center"| | ||
| Line 98: | Line 98: | ||
|align="right"| | |align="right"| | ||
{| | {| | ||
| − | | E-ring | + | | E-ring cyclization<br/>(from 18α) |
| [[Image:Arrow00dl.png]] | | [[Image:Arrow00dl.png]] | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 106: | Line 106: | ||
|E-ring<br/> | |E-ring<br/> | ||
|[[Image:Arrow00d.png]] | |[[Image:Arrow00d.png]] | ||
| − | | | + | |cyclization<br/>(from 18β) |
|} | |} | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | lanosteryl cation<br/>[[Image:Lanosteryl cation.png]] | + | | lanosteryl cation <small>(C-C-C)</small><br/>[[Image:Lanosteryl cation.png]] |
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | H18β-lupyl cation<br/>[[Image:Lupyl cation2.png]] | + | | H18β-lupyl cation <small>(C-C-C-B)</small><br/>[[Image:Lupyl cation2.png]] |
| | | | ||
| − | | H18α-lupyl cation<br/>[[Image:Lupyl cation.png]] | + | | H18α-lupyl cation <small>(C-C-C-C)</small><br/>[[Image:Lupyl cation.png]] |
|- | |- | ||
|align="center"| | |align="center"| | ||
Revision as of 04:32, 9 August 2010
Contents |
Triterpene (C30) Classes
Ring configuration
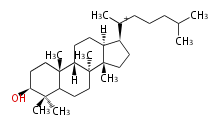
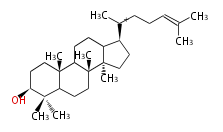
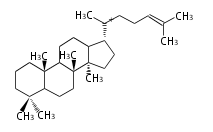
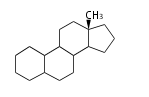
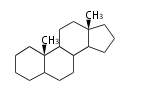
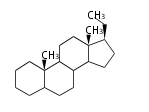
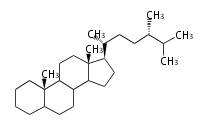
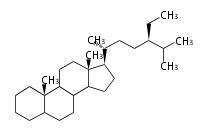
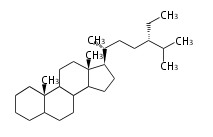
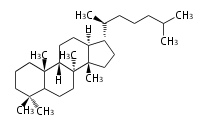
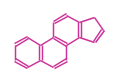
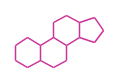
The basic structure is 4 carbon rings, cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene, gonane, or sterane. The rings B/C are always trans in all natural steroids. If the rings C/D are trans, it is called gonane. If its stereochemistry is unspecified, it is called sterane. Most steroids take gonane form, but in cardenolides and bufanolides, the rings C/D are cis.
 |
|
| Cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene | Gonane |
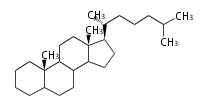
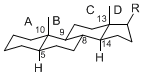
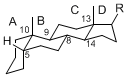
The majority of steroids have methyl groups sticking out from the bridgehead positions C-10 and C-13. When these methyl groups (or hydrogens) stand above the plane, they are called β-configuration. Those below the plane are called α-configuration. If the configuration at any site is unknown, it is indicated as ξ (Greek Xi). By default, hydrogen atoms or substituents at the positions C-8, 9, 10, 13, and 14 are assumed to be 8β, 9α, 10β, 13β, and 14α configurations. C-5 is a special position, because there are as many 5α steroids as 5β are.
 |
 |
|
| cholestane backbone | 5α-configuration | 5β-configuration |
Biosynthesis
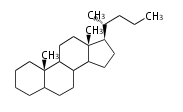
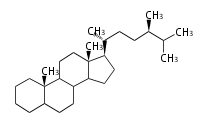
The starting point is squalene, which is formed by joining two FPPs tail-to-tail. Bacterial cyclases use squalene directly, but those of the other species use 2,3-oxidosqualene for cyclization.
- In bacteria, squalene is cyclized via the 17α-deoxydammarenyl cation to hopene and other triterpenes[1].
- In eukaryotes, 2,3-oxidosqualene is cyclized via the protosteryl cation to lanosterol (animals and fungi) or cycloartenol (plants) by a series of 1,2-hydride and methyl shifts (Wagner-Meerwein shifts).[2]
- In plants, various triterpenes arise from the dammarenyl cation.
| ANIMALS, FUNGI, and YEAST | PLANTS | |||||||||||
| 2,3-oxidosqualene | ||||||||||||
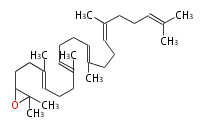
| ||||||||||||
| lanosterol |
lupeol | |||||||||||
| 17β-protosteryl cation (C-B-C)[4] | D-ring expansion + E-ring cyclization (from 18α/17β) |
hancolupyl cat. (C-B-C-C) arborinyl cation (C-B-C-C) 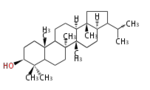
|
17β-dammarenyl cation (C-C-C)[5] | D-ring expansion |
baccarenyl cation (C-C-C-C)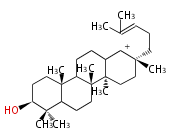
| |||||||
|
|
| ||||||||||
lanosteryl cation (C-C-C)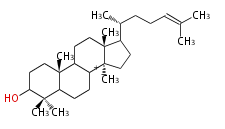
|
H18β-lupyl cation (C-C-C-B)
|
H18α-lupyl cation (C-C-C-C)
| ||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
cucurbitenyl cation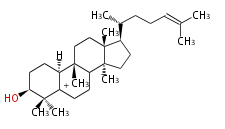
|
lupeol
|
|||||||||||
| Examples. All steroids including steroidal saponins |
Examples. all triterpenoids and saponins |
|||||||||||
- ↑ Bacterial squalene cyclases can accept oxidosqualene as their substrates, but oxidosqualene usually does not exist in bacteria
- ↑ A trace amount of phytosterols comes from lanosterol. Ohyama K, Suzuki M, Kikuchi J, Saito K, Muranaka T (2009) Dual biosynthetic pathways to phytosterol via cycloartenol and lanosterol in Arabidopsis Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(3):725-730
- ↑ The most accessible enzyme among oxidosqualene cyclases.
Ref. Corey EJ, Russey WE, Ortiz-de-Montellano PR (1966) 2,3-Oxidosqualene, an intermediate in the biological synthesis of sterols from squalene J Am Chem Soc 88:4750-1 - ↑ The rings of protosteryl cation are chair-boat-chair configuration. The C-17 chain is β-configuration, not α.
Ref. Corey EJ, Virgil SC (1991) An experimental demonstration of the stereochemistry of enzymic cyclization of 2,3-oxidosqualene to the protosterol system, forerunner of lanosterol and cholesterol. J Am Chem Soc 113:4025-6 - ↑ The rings of dammarenyl cation are all-chair configuration. The C-17 chain is β-configuration.
Ref. Xiong Q, Rocco F, Wilson WK, Xu R, Ceruti M, Matsuda SPT (2005) Structure and reactivity of the dammarenyl cation: configuration transmission in triterpene synthesis. J Org. Chem. 70:5362-75
Useful Reviews:
- Xu R, Fazio GC, Matsuda SPT (2004) On the origins of triterpenoid skeletal diversity. Phytochemstry 65:261-291 PMID 14751299
| BACTERIA | |
| squalene | |
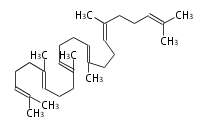
|
|
| squalene-hopene |
|
| 17α-deoxydammarenyl cation[2] | |
| D-ring |
|
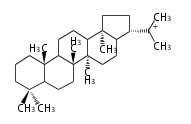
|
|
| |
|
hopene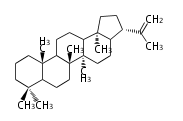
|
|
| Examples. |
Design of Tri-terpene ID numbers ID番号の設計
12-DIGIT
| T | P | 3 | x | y | y | r | h | g | n | c | c |
- x ... species information
| Symbol at x | Kingdom | Phyla | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | Animalia | Arthropoda (Insects, crabs) | ecdysteroids |
| V | Chordate (Vertebrates) | sex steroids, corticosteroids, anabolic steroids | |
| O | Others | marine steroids | |
| P | Plantae | Phytosterols | lanosterols, cholesterols, brassinolides |
| S | Saponins | saponins | |
| F | Fungi | ergosterols | ergosterols |
| B | Bacteria | bacterial sterols | hopanoids |
- y ... backbone structure (母核構造)
- r ... number of major rings (環構造数)
Click above categories to see details.
- h ... hydroxylation pattern (水酸基数)
Click above categories to see details.
- g ... glycosylation pattern(糖修飾パターン)
Click above categories to see details.
- n ... number of sugars (修飾糖数)
Click above categories to see details.
- c ... serial number (通し番号)
Cite error:
<ref> tags exist, but no <references/> tag was found
This category currently contains no pages or media.